As the sun rises over the vast expanses of Pakistan, its golden rays illuminate not just the landscapes but also the burgeoning crisis that threatens the very fabric of this vibrant nation. In a land where rivers once flowed with life and the earth brimmed with agricultural promise, the specter of a water shortage looms ominously on the horizon. With population growth, climate change, and mismanagement converging to form a perfect storm, Pakistan finds itself at a critical juncture—grappling with a water crisis that has implications far beyond mere resources. It poses a significant humanitarian challenge, one that demands urgent attention and thoughtful solutions. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of Pakistan’s water crisis, exploring its roots, impacts, and the collective responsibility to forge a sustainable path forward. The time for action is now, as the fight for water becomes a fight for life itself.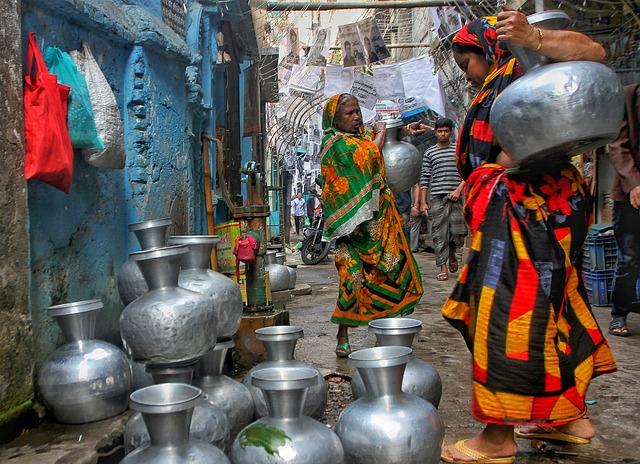
Exploring the Roots of Pakistans Water Scarcity and Its Impact on Communities
Water scarcity in Pakistan is a multifaceted crisis that has deep historical, environmental, and socio-economic roots. Geographically, the nation is traversed by the Indus River System, which has been the lifeblood of its agriculture and livelihoods. However, overexploitation and mismanagement of water resources, compounded by climate change impacts such as decreasing rainfall and rapid glacier melt, have led to severe shortages. This crisis does not affect all regions equally; communities in rural areas especially bear the brunt, facing dwindling supplies for irrigation and drinking. Inadequate infrastructure and poor governance exacerbate the situation, leaving many regions without reliable access to this essential resource. As cities expand and industrial demands rise, the competition for water intensifies, creating further challenges for sustainability.
The social ramifications of this crisis are far-reaching, affecting daily life and health. Water scarcity has driven many communities to adopt coping strategies that often inflict greater strain on women and children, who typically bear the burden of water collection. The World Health Organization has reported a rise in waterborne diseases as families turn to unsafe sources due to the scarcity of clean water. In response, several grassroots movements have emerged, advocating for better water management and equitable distribution policies. Furthermore, community-based initiatives are encouraging rainwater harvesting and the promotion of efficient irrigation techniques to foster resilience. Ultimately, a collaborative effort that engages local communities, government authorities, and international stakeholders is essential to mitigate the impact of water scarcity and pave the way for a more sustainable future.

Innovative Solutions: Harnessing Technology for Sustainable Water Management
In the face of Pakistan’s escalating water crisis, innovative technological advancements are emerging as vital tools for sustainable management of water resources. Smart irrigation systems are gaining traction, utilizing sensors and data analytics to optimize water usage, ensuring that agriculture—Pakistan’s mainstay—uses only the necessary amount of water. Furthermore, rainwater harvesting technologies are being implemented in urban and rural settings, enabling communities to capture and store rainwater for household use, thereby reducing reliance on over-exploited groundwater sources. The integration of geographic information systems (GIS) aids in mapping water resources accurately, helping policymakers make informed decisions for equitable distribution and conservation efforts.
Renewable energy solutions, such as solar-powered desalination plants, are also being explored to convert saline water into potable water, offering hope for arid regions grappling with severe shortages. To facilitate these advancements, partnerships between local governments, private sectors, and international organizations are essential. An organized approach can enhance community awareness and implementation of water-saving technologies. Here’s a brief overview of some key technologies contributing to sustainable water management:
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Irrigation | Automated systems that adjust water delivery based on plant needs. | Reduces water waste, improves crop yields. |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Systems designed to collect and store rainwater. | Enhances water availability, lowers costs. |
| GIS Mapping | Geo-spatial technologies for tracking water resources. | Improved resource management and planning. |
| Solar Desalination | Renewable technology to convert seawater to freshwater. | Provides clean water in water-scarce regions. |

Empowering Local Communities: The Role of Education and Advocacy in Water Conservation
Education serves as a vital tool in shaping awareness and fostering proactive behaviors among local communities regarding water conservation. By integrating water resource management into school curricula, communities can cultivate a generation that values sustainability. Workshops, seminars, and community discussions can further elevate this knowledge, equipping individuals with the skills to effectively monitor and manage local water supplies. Additionally, collaboration with local NGOs can amplify these efforts, facilitating access to workshops led by experts who can impart advanced techniques in water collection and purification. Local heroes in the form of trained volunteers can emerge from these initiatives, spreading the word and spearheading change in their neighborhoods.
Advocacy also plays a pivotal role in mobilizing communities toward effective water conservation practices. Grassroots campaigns that focus on local hydration challenges can underscore the urgency of each community’s water issues. Strategies such as community clean-up drives, water-saving challenges, and educational fairs can galvanize public interest and involvement. The formulation of local water committees can empower residents to engage in policy discussions with government entities, ensuring community voices are heard in water management strategies. To visualize the importance of community engagement, the table below showcases successful advocacy projects from various localities:
| Project Name | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Save Our Streams | Lahore | Increased local river bank protection by 50% |
| Water Wise Families | Khanewal | Reduced household water usage by 30% |
| Green Pakistan Initiative | Multan | Engaged 1,000+ volunteers in tree planting near water bodies |

A Collaborative Path Forward: Engaging Stakeholders in Comprehensive Water Policy Reform
As Pakistan grapples with an escalating water crisis, the significance of engaging stakeholders is paramount. The solution isn’t solely in policy amendments but rather in fostering a collaborative environment that bridges disparate sectors. This requires the active participation of various groups, including governmental agencies, local communities, NGOs, and the private sector. Each stakeholder brings unique insights and resources to the table, enabling the development of a comprehensive framework that addresses both immediate needs and long-term sustainability. Consider the following critical collaboration aspects:
- Inclusive Dialogue: Establishing platforms for open discussions ensures that every voice is heard, enhancing policy formulation.
- Shared Resources: Pooling financial, educational, and technological resources can lead to innovative solutions.
- Community Empowerment: Engaging local communities in decision-making not only fosters trust but also promotes ownership of water resources.
Moreover, creating structured partnerships can facilitate informed decision-making. Regular workshops and seminars can be organized to share best practices and research findings related to water management. To aid in this, a concise overview of stakeholder roles may serve as a visual guide:
| Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|
| Government | Policy formulation and regulation |
| Local Communities | Implementation and feedback |
| NGOs | Aid and education on conservation |
| Private Sector | Investment in infrastructure |
Through multi-faceted engagement and shared responsibility, stakeholders can pave a way forward that not only addresses the urgent crisis but also lays the groundwork for future resilience against water scarcity in Pakistan.
In Retrospect
As we conclude our exploration of Pakistan’s water crisis, it becomes evident that this issue transcends borders and institutions; it is fundamentally a matter of humanity and survival. The intricate web of challenges faced by the nation demands not just immediate attention but also long-term commitment to sustainable solutions. While the currents of change may seem slow, every drop of effort counts. From grassroots advocacy to policy reform, there exists a pathway towards revitalizing Pakistan’s water resources and, ultimately, its people.
Collectively, we must recognize that the fight against water scarcity is not solely about infrastructure or international aid; it is about empowering communities, fostering resilience, and nurturing a future where access to clean water is a right rather than a privilege. As we look to the horizon, it is crucial to engage in this dialogue persistently, for the health of Pakistan is intertwined with the health of the planet. Let us strive to turn the tide and inspire action, ensuring that water, the essence of life, flows freely into the hands of those who need it most. The time to act is now, for the solution to this looming humanitarian challenge lies not in the darkness of despair, but in the light of collective resolve and innovation.



